Introduction
The advancement of medical technology has revolutionized the way healthcare professionals diagnose and treat various conditions. Among these innovations, tissue contact probe ablators have emerged as a critical tool in modern medicine, particularly in surgical procedures. These devices, designed to deliver energy directly to tissues for the purpose of destruction, coagulation, or vaporization, play a vital role in treating a range of medical conditions.
Definition
Tissue contact probe ablation is a medical procedure that applies controlled heat or cold, usually within the body, to specific tissue using specialised probes. These probes allow for the exact ablation of tissues, such as tumours or aberrant cells, using cryotherapy or heat radiation. They are frequently utilised in minimally invasive procedures like radiofrequency ablation, which is used to treat illnesses like cardiac arrhythmias or cancer.
Understanding Tissue Contact Probe Ablators
Tissue contact probe ablators are specialized medical devices used in minimally invasive procedures. They deliver energy, such as radiofrequency (RF), microwave, or laser, directly to the targeted tissue. This energy causes the tissue to heat up, leading to its destruction or modification. The precision of these devices allows surgeons to target specific areas while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Key Features of Tissue Contact Probe Ablators:
-
Energy Delivery: Various forms of energy, such as RF, microwave, or laser, are utilized depending on the procedure and tissue type.
-
Minimally Invasive: These devices enable surgeons to perform procedures with minimal incisions, reducing recovery time and risk of complications.
-
Precision: Tissue contact probe ablators offer high precision, targeting only the desired tissue while sparing adjacent healthy structures.
-
Versatility: They are used in a wide range of medical fields, including oncology, cardiology, and orthopedics.
Applications of Tissue Contact Probe Ablators in Modern Medicine
Tissue contact probe ablators have found widespread application across multiple medical specialties, contributing significantly to the treatment of various conditions. Their versatility and effectiveness have made them indispensable in both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Oncology: In oncology, tissue contact probe ablators are used for the treatment of various cancers through a process known as ablation. Ablation therapy involves the destruction of cancerous tissue using heat, cold, or chemical agents. Tumours of the liver, lungs, kidneys, and bones are frequently treated with radiofrequency and microwave ablation. These methods provide a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery, offering patients quicker recovery times and fewer complications.
-
Liver Tumors: RF ablation is particularly effective in treating small liver tumors that are not amenable to surgical removal. The ablator is inserted directly into the tumor, and the energy delivered destroys the cancerous cells.
-
Lung Tumors: Microwave ablation is often used to treat early-stage lung cancers or tumors that cannot be surgically removed. The precision of the ablation reduces the risk of damage to healthy lung tissue.
Cardiology: In cardiology, tissue contact probe ablators are primarily used in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation (AF). Catheter ablation, a procedure where the ablator is guided to the heart through blood vessels, is employed to destroy small areas of heart tissue that are responsible for abnormal electrical signals.
-
Atrial Fibrillation: Catheter ablation has become a standard treatment for patients with AF who do not respond to medication. The ablation procedure targets the areas of the heart that trigger irregular rhythms, restoring normal heart function.
-
Ventricular Tachycardia: In cases of ventricular tachycardia, a life-threatening arrhythmia, catheter ablation can be used to remove the areas of the heart that generate rapid, abnormal heartbeats.
Gastroenterology: Tissue contact probe ablators are also utilized in gastroenterology for the treatment of conditions such as Barrett’s esophagus and certain types of gastrointestinal tumors. Endoscopic ablation techniques, where the ablator is introduced through the mouth or rectum, offer a minimally invasive approach to treating these conditions.
-
Barrett’s Esophagus: This condition, which can lead to esophageal cancer, is often treated with RF ablation. The procedure removes the abnormal tissue, reducing the risk of cancer development.
-
Gastrointestinal Tumors: Ablation techniques are used to treat tumors in the digestive tract that are difficult to reach surgically. The use of ablation provides a targeted approach, sparing healthy tissue.
Orthopedics: In the field of orthopedics, tissue contact probe ablators are used in the treatment of conditions like osteoid osteoma, a benign bone tumor. The ablation process involves the destruction of the tumor through heat generated by RF or laser energy, providing pain relief and preventing the tumor’s growth.
-
Osteoid Osteoma: The best treatment for this problem is radiofrequency ablation. Quick return to normal activities is possible for patients after the minimally invasive surgery, which can be done as an outpatient.
Urology: In urology, tissue contact probe ablators are used for the treatment of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). These procedures involve the destruction of prostate tissue to relieve symptoms or eradicate cancer cells.
-
Prostate Cancer: Ablation techniques such as high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) are used to treat localized prostate cancer. This approach offers a less invasive option compared to traditional surgery.
-
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Ablation procedures like transurethral needle ablation (TUNA) use RF energy to reduce the size of the prostate, alleviating symptoms of BPH.
Benefits of Tissue Contact Probe Ablators
The integration of tissue contact probe ablators into modern medicine has brought numerous benefits to both patients and healthcare providers. Their ability to deliver precise, controlled treatment has improved patient outcomes and expanded the range of conditions that can be treated minimally invasively.
Enhanced Precision: One of the most significant advantages of tissue contact probe ablators is their ability to target specific tissues with great precision. This minimizes collateral damage to surrounding healthy tissues, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster recovery.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Tissue contact probe ablators allow for minimally invasive procedures, which are associated with shorter hospital stays, less pain, and quicker recovery times. This is particularly beneficial for patients who may not be candidates for traditional surgery due to age or other health conditions.
Reduced Complications: The use of tissue contact probe ablators often results in fewer complications compared to traditional surgical approaches. The precise delivery of energy limits the extent of tissue damage, reducing the risk of infection, bleeding, and other postoperative issues.
Broad Range of Applications: These devices are versatile and can be used in various medical fields, from oncology to cardiology. This broad applicability makes them valuable tools in treating a wide range of conditions.
Improved Patient Outcomes: The use of tissue contact probe ablators has been associated with improved patient outcomes, including higher success rates and lower recurrence rates for certain conditions. Patients benefit from less invasive treatment options that still offer effective results.
Challenges and Future Directions
While tissue contact probe ablators have brought significant advancements to modern medicine, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. These include the high cost of the devices, the need for specialized training, and potential limitations in treating certain complex conditions.
Cost: The high cost of tissue contact probe ablators can be a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in resource-limited settings. Efforts to reduce costs and make these devices more accessible will be crucial in expanding their use.
Training: The effective use of tissue contact probe ablators requires specialized training for healthcare providers. Ensuring that medical professionals are adequately trained is essential for maximizing the benefits of these devices.
Technological Advancements: As technology continues to evolve, the development of more advanced tissue contact probe ablators is expected. These innovations may include improvements in energy delivery, better imaging guidance, and enhanced safety features.
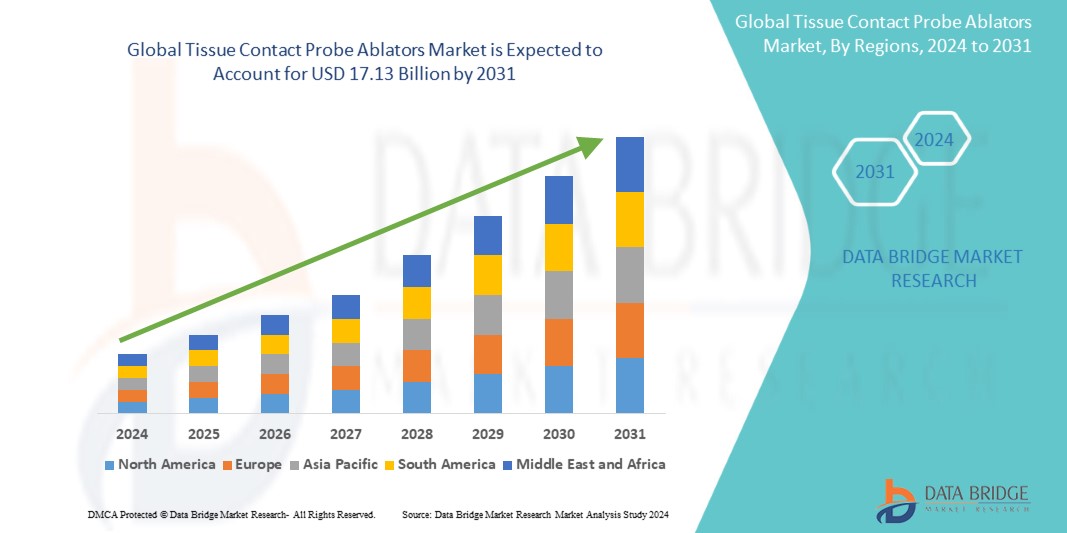
Growth Rate of Tissue Contact Probe Ablators Market
The size of the worldwide market for tissue contact probe ablators was estimated at USD 5.88 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.30% from 2024 to 2031, reaching USD 17.13 billion.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-tissue-contact-probe-ablators-market
Conclusion
Tissue contact probe ablators represent a significant advancement in modern medicine, offering precise, minimally invasive treatment options for a wide range of conditions. Their role in improving patient outcomes, reducing complications, and expanding the possibilities for minimally invasive procedures cannot be overstated. As technology continues to advance, the potential for tissue contact probe ablators to revolutionize healthcare will only grow, providing patients with safer, more effective treatment options.